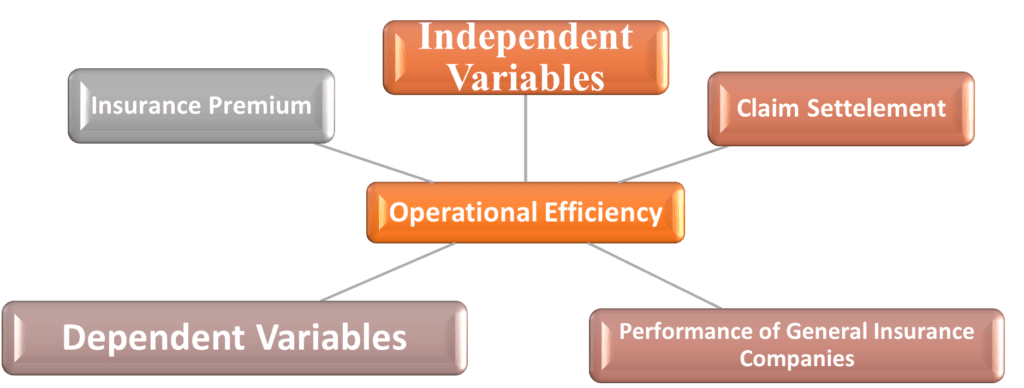
The objective of this paper is to assess the operational GENERAL INSURANCE effectiveness of Indian companies using Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA). Insurers were given efficiency scores, and efforts were made to identify the best Public and General Insurers. The preliminary findings indicated that, in terms of operational effectiveness, General Insurers are more adept at selecting the scale size. The general insurer exhibits inefficiency in their operational and investment decisions based on their overall average efficiency. When evaluating the two models under consideration, super efficiency ratings and decision ranking produce some inconsistent findings.
Indian General Insurance Company
Life insurance is closely followed by general insurance. People today are more protective of their assets and are doing everything they can to safeguard them. Whenever there is an accident, general insurance kicks in general insurance is therefore equally crucial backed by life insurance.
Simply put, general insurance offers a layer of financial protection for the assets it insures against natural disasters, sickness, any sort of medical emergency, accidents, bad luck, etc. Any non-life insurance coverage falls under this category insurance in general. There are basically four broad groups. broader insurance they are the best health insurer, second-place auto insurance and third-place vacation insurance fourth, home insurance, and naturally there are These four categories stand out among many others. Public sector general insurance businesses are dealing with many obstacles from private players and must endure even after finishing, they have made significant progress in their quality of service in various areas, such as lowering the premium, prompt resolution of disputes, etc.
Expert Thoughts
Jawahar Babu (2010): The overall influences on claims settlements in vehicle insurance offered by third party agents are the main subject of this study. The majority of issues are resolved through legal proceedings, which unusually delays settlement. This is also a result of the rise in traffic collisions. This study specifically examined the claim settlement process.
K. Rajender et.al. (2012): The researchers in this study concentrated on the general insurance companies’ investment practices. Both parameters related to terms and those related to security are thoroughly examined. In general, this study concentrated on how insurance premium money should be invested to increase the returns on the portfolios.

Saroji Hiremath (2013): In this study, the researcher concentrated on new patterns and issues that general insurance businesses in India were facing, particularly those brought on by diverse and personalized service patterns from global insurance companies. Despite the fact that there are more competitors in the general insurance sector, India is a vast market with plenty of room for expansion.
S. Anoop Kumar (2014) : In this study, the researcher focuses on the method general insurance firms use to determine the loss by taking into account motor claims for parts and other unrelated claims. According to the study, for the purposes of applying depreciation, all elements created using composite materials are considered to be other parts.
Bhardwaj Geeta et.al. (2015): The study’s primary focus was on health insurance fraud and its difficulties. The researcher acknowledged the method for successfully avoiding fraud. The company should implement a top-down strategy based on the actual impact the risk has on their operations. It looks into how many fraud cases there are in India and finds that opportunistic, organized, and repeat fraudsters account for 15% of all claims. Fraud that was committed from the perspective of the insurer and the insured was frequently evaluated fraud.
Life insurance industry recorded a premium income of ₹6.29 lakh crore during 2020-21 as against ₹5.73 lakh crore in the previous financial year, registering growth of 9.74 per cent (12.75 per cent in 2019-20). While private sector insurers posted 16.50 per cent growth (13.42 per cent in LIC 3,79,389.60 4,03,286.55 66.22 64.14 (12.41) (6.30) Private Sector 1,93,520.59 2,25,444.48 33.78 35.86 (13.42) (16.50) Total 5,72,910.19 6,28,731.04 100.00 100.00 (12.75) (9.74) Table 1 Premium Underwritten by Life Insurers Insurer Premium (₹crore) Market Share (%) 2019-20 2020-21 2019-20 2020-21.
Note: Figures in bracket indicates growth (in per cent) over previous year. 2019-20) in their premium income, LIC recorded 6.30 per cent growth (12.41 per cent in 2019-20). Premium underwritten by LIC and private sector is provided in Table 1 and insurer wise is provided in Statement 3.

The life insurance industry paid benefits of ₹3.99 lakh crore in 2020-21 (₹3.51 lakh crore in 2019-20) constitutes 63.42 per cent of the gross premium underwritten (61.35 per cent in 2019-20). The benefits paid by the private insurers was ₹1.13 lakh crore (₹98,706 crore in 2019-20) constituting 50.15 per cent of the premium underwritten (51.01 per cent in 2019-20). LIC paid benefits of ₹2.86 lakh crore in 2020-21, constituting 70.85 per cent of the premium underwritten (₹2.53 lakh crore in 2019- 20, 66.62 per cent of the premium underwritten).
The benefits paid on account of surrenders / withdrawals increased to ₹1.29 lakh crore in 2020-21 (₹1.17 lakh crore in 2019-20), of which LIC accounted for 61.89 per cent and remaining 38.11 per cent by private sector. In the current year, in case of LIC, out of the ₹80,101 crore surrenders, ULIP policies accounted for ₹2,619 crore (3.27 per cent) as against ₹3,106 crore (4.43 per cent) in 2019-20. In case of the private insurers, the ULIP surrenders accounted for ₹40,025 crore (72.82 per cent) in 2020-21 as against ₹38,327 crore (73.96 per cent) in 2019-20.

The goal of this study is to assess the performance of particular general insurance providers. General insurance businesses in the public sector are required to adopt new and creative policies to advance the expansion in order to compete with private players. The growth of the general insurance industry in India, so only a good beginning has been made thus far; the remaining 90% of the inhabitants of India.
It is a young, evergreen plant. If they concentrate, the insurance industry will grow. people as are learning about insurance-related products and services, the governing body, or the Insurance Regulatory Development Authority (IRDA) should prioritize defending the interests of the people by establishing standard regulations that both public and private sectors must adhere to firms that provide general insurance.