Bloom’s Taxonomy and New Teaching-Learning Methods: A Modern Approach to Education
In the ever-evolving field of education, Bloom’s Taxonomy remains a foundational framework for structuring learning objectives and assessing student performance. Combined with innovative teaching and learning methods, it equips educators to foster critical thinking, creativity, and deep understanding among students. Let’s explore Bloom’s Taxonomy and how it integrates with modern pedagogical practices.
Bloom’s taxonomy is a framework that categorizes different levels of thinking from lower-order to higher-order. It’s a valuable tool for educators, trainers, and anyone who wants to design effective learning experiences.
What is Bloom’s Taxonomy?
Bloom’s Taxonomy, developed by Benjamin Bloom in 1956, is a hierarchical classification of cognitive learning objectives. It categorizes educational goals into six levels, moving from basic knowledge acquisition to complex, abstract thinking.
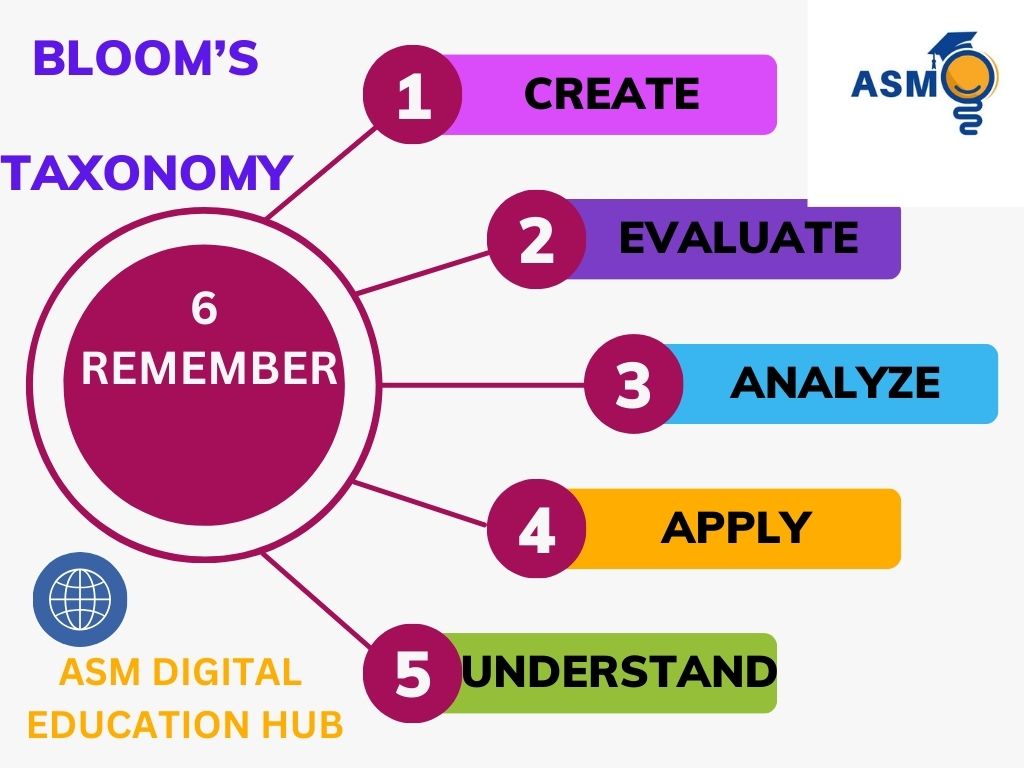
The Six Levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy
- Remember: Recalling facts and basic concepts. (e.g., Define, List, Recall)
- Understand: Explaining ideas or concepts. (e.g., Summarize, Describe, Discuss)
- Apply: Using knowledge in new situations. (e.g., Solve, Implement, Demonstrate)
- Analyze: Breaking down information to examine relationships. (e.g., Compare, Contrast, Categorize)
- Evaluate: Making judgments based on criteria. (e.g., Critique, Justify, Recommend)
- Create: Producing new or original work. (e.g., Design, Construct, Invent)
Modern Teaching-Learning Methods Aligned with Bloom’s Taxonomy
To meet the demands of 21st-century education, teaching methods must go beyond traditional lectures and integrate innovative strategies that align with Bloom’s Taxonomy.
1. Active Learning
- Description: Students actively participate in the learning process through discussions, problem-solving, and hands-on activities.
- Application:
- Understand: Conduct group discussions on a topic.
- Apply: Solve case studies or real-world problems.
2. Flipped Classroom
- Description: Students study materials (videos, articles) at home and engage in collaborative activities in class.
- Application:
- Remember: Watch instructional videos before class.
- Analyze: Debate the pros and cons of a concept during class discussions.
3. Project-Based Learning (PBL)
- Description: Students work on projects over time, solving complex problems and producing tangible outcomes.
- Application:
- Create: Design a sustainable city model as part of an environmental science project.
- Evaluate: Present findings to peers and justify decisions.
4. Gamification
- Description: Incorporating game elements like challenges, leaderboards, and rewards into lessons.
- Application:
- Apply: Use simulation games to demonstrate economic principles.
- Analyze: Reflect on strategies used during gameplay.
5. Inquiry-Based Learning
- Description: Encourages students to ask questions, explore, and discover answers independently or collaboratively.
- Application:
- Understand: Research and discuss a topic based on guiding questions.
- Evaluate: Assess the validity of different sources of information.
6. Technology Integration
- Description: Leveraging tools like AI, virtual reality (VR), and learning management systems (LMS) to enhance learning.
- Application:
- Remember: Use quizzes and flashcards on LMS platforms.
- Create: Develop a VR tour of historical landmarks.

Why Integrate New Methods with Bloom’s Taxonomy?
- Engages Diverse Learners: Modern methods cater to different learning styles and preferences.
- Promotes Higher-Order Thinking: Activities are designed to progress from remembering to creating.
- Prepares for Real-World Challenges: Students develop critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills.
- Encourages Lifelong Learning: Inquiry and project-based approaches inspire curiosity and self-directed learning.
Practical Tips for Educators
- Start Small: Incorporate one or two methods and expand gradually.
- Align Activities: Map each activity to a level of Bloom’s Taxonomy for structured learning.
- Leverage Feedback: Use formative assessments to refine methods and ensure they meet learning objectives.
- Foster Collaboration: Encourage group activities to build teamwork and communication skills.
Conclusion
Bloom’s Taxonomy, when paired with modern teaching-learning methods, transforms the educational experience. It helps educators design meaningful lessons that foster deep understanding and practical application. As education continues to evolve, these strategies will remain essential for nurturing well-rounded, innovative thinkers.
Start applying Bloom’s Taxonomy with these modern methods and empower your students to achieve their highest potential!
Here’s a breakdown of the basic level of Bloom’s taxonomy:
1. Remember:
- Focus: Recalling facts, terms, definitions, and basic information.
- Keywords: List, define, name, recall, repeat, identify.
- Examples:
- “What is the capital of France?”
- “Name the three branches of government.”
- “List the five steps in the scientific method.”
2. Understand:
- Focus: Grasping the meaning of information, explaining concepts in your own words.
- Keywords: Describe, explain, interpret, translate, illustrate.
- Examples:
- “Explain the difference between photosynthesis and respiration.”
- “Describe the main events of the French Revolution.”
- “Create a diagram to illustrate the water cycle.”
3. Apply:
- Focus: Using knowledge and skills in new situations, solving problems.
- Keywords: Use, apply, implement, practice, solve.
- Examples:
- “Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the missing side of a triangle.”
- “Write a paragraph summarizing the main points of the article.”
- “Create a budget to save money for a new phone.”
Remember:
- These are just the basic levels of Bloom’s taxonomy. There are three more levels: Analyze, Evaluate, and Create.
- The levels are hierarchical, meaning each level builds on the previous one.
- Effective learning experiences should incorporate activities at all levels of the taxonomy.
Tips for using Bloom’s taxonomy:
- Start with the end in mind. What do you want your learners to know and be able to do?
- Use Bloom’s verbs to write clear learning objectives.
- Design activities that match the desired level of thinking.
- Vary your instruction and assessment methods.
- Reflect on your teaching and make adjustments as needed.
By using Bloom’s taxonomy, you can create learning experiences that are both challenging and rewarding for your learners.
Resources that you may find helpful:


Very useful information
This is interesting